Outline
I try to develop the server-side with python django. in this blog, I’ll introduce how to create new application in django, and how to make and use Models for storing the data required in the application.
this blog is a series. if you want to check other blog posts of the series, see the links below.
- django installation
- Start django Project
- Use Models in django
- django Administrator Page
- django Routing
- django ORM
- django View
- django Form
- Upload django project to Heroku
also, this blog series source code is opened on Github. you can see full source code via the link below.
Create django Application
django has a big unit called Project and a small unit called Application. one project can have many applications. in this blog, we’re going to develop a blog with django. execute the django command below to create blog application.
# virtualenv venv
# source venv/bin/activate
# pip install -r requirements.txt
# django-admin --version
# 2.2
python manage.py startapp blogafter creating, you can see the folder structure like below.
|-- django_exercise
| |-- __init__.py
| |-- settings.py
| |-- urls.py
| |-- wsgi.py
|-- blog
| |-- __init__.py
| |-- admin.py
| |-- apps.py
| |-- models.py
| |-- tests.py
| |-- views.py
|-- manage.pynew files in the application folder do the following.
- admin.py: Admin page configurations file that django basically provides.
- apps.py: Application main file
- models.py: Application Models file
- tests.py: test file
- views.py: Application Views file
there are other files that are used in django.
- urls.py: Application url management file
- forms.py: input form file
- behaviors.py: Model mixin option file
- constants.py: Application constant file
- decorators.py: decorator file
- factories.py: test data factory file
- helpers.py: Vies and Models helper function file
- managers.py: custom model manager file
- signals.py: custom signal file
- viewmixins.py: Views mixin file
I have no idea what they are. we’ll study one by one after, so we just check these files are existed and move on.
we’ve created django application, so we need to register the application to django project. open django_exercise/settings.py and modify it like below to register the application.
...
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'blog'
]
...Create Models
let’s see how to create Models to develop the blog site. open blog/models.py and add the codes below.
from django.db import models
from django.utils import timezone
class Post(models.Model):
author = models.ForeignKey('auth.User', on_delete=models.CASCADE)
title = models.CharField(max_length=100)
content = models.TextField()
created_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
updated_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now=True)
published_at = models.DateTimeField(blank = True, null = True)
def publish(self):
self.published_at = timezone.now()
self.save()
def __str__(self):
return self.titlelet’s see details.
Posthasauthor, title, content, created_at, updated_at, published_atfields- we use
ForeignKeyfunction forauthorto referrerUsermodel ofauthapplication that django basically provides.(auth.User: AppName.Model) - we use
CharFieldfunction to store fixed-length string type fortitlefield. we setmax_lengthoption to store 100 length string. contentis the blog post content field created byTextFieldto store not fixed-length textcreated_atis the blog post create date created byDateTieFieldfunction to store date and time. we usedauto_now_addoption to store create time when the data create.updated_atwill be the blog post modification date field.auto_nowoption makes it store update time when the data updated.published_atis the blog post publish date field.
I didn’t explain about blank = True, null = True because I think I need to explain separately.
blank: this option is related to the validation. when we useform.is_valid()to validate input data, this options will be used. the data can beblank.null: this is related to the database. this option allows the data can be null.(nullable)
this model has publish, __str__ functions.
publish: this is for the publish feature in the blog post service. when we publish the blog post by using this function, the blog post data’spublished_atwill be updated.__str__: this is the standard python class method that returns human-readable string.
Create Table By Models
let’s see how to create database table by Models that we created.
Create Migration File
first, we need to create migration file for creating database table by our Models. execute the django command below to create the migration file
python manage.py makemigrations blogafter executing, you can see the result like below.

and, also you can see the migration folder and files are created.
|-- django_exercise
| |-- __init__.py
| |-- settings.py
| |-- urls.py
| |-- wsgi.py
|-- blog
| |-- migrations
| | |-- __init__.py
| | |-- 0001_initial.py.py
| |-- __init__.py
| |-- admin.py
| |-- apps.py
| |-- models.py
| |-- tests.py
| |-- views.py
|-- manage.pyCreate Table
execute the django command to create the table by the migration that is created by Models.
python manage.py migrate blogafter executing, you can see the result like below.

if you use database tool, you can see the table we created.
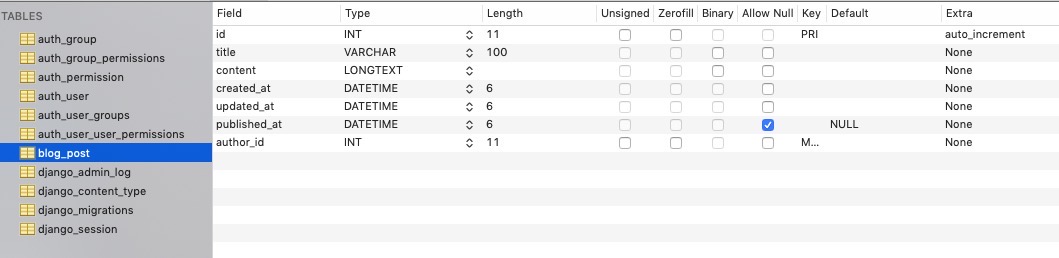
Completed
Done! we’ve seen how to create django Models and create the database table by Models. now, we’re ready to store data for developing. let’s design DB and make Models and Migration files belong to it!
Reference
- Model Data Type: https://www.webforefront.com/django/modeldatatypesandvalidation.html
Model Data Type
you cna use the model types below in django.
| Data type | Django model type |
|---|---|
| Binary | models.BinaryField() |
| Boolean | models.BooleanField() |
| Boolean | models.NullBooleanField() |
| Date/time | models.DateField() |
| Date/time | models.TimeField() |
| Date/time | models.DateTimeField() |
| Date/time | models.DurationField() |
| Number | models.AutoField() |
| Number | models.BigIntegerField() |
| Number | models.DecimalField(max_digits=X,decimal_places=Y) |
| Number | models.FloatField() |
| Number | models.IntegerField() |
| Number | models.PositiveIntegerField() |
| Number | models.PositiveSmallIntegerField() |
| Number | options.SmallIntegerField() |
| Text | models.CharField(max_length=N) |
| Text | models.TextField() |
| Text (Specialized) | models.CommaSeparatedIntegerField(max_length=50) |
| Text (Specialized) | models.EmailField() |
| Text (Specialized) | models.FileField() |
| Text (Specialized) | models.FilePathField() |
| Text (Specialized) | models.ImageField() |
| Text (Specialized) | models.GenericIPAddressField() |
| Text (Specialized) | models.SlugField() |
| Text (Specialized) | models.URLField() |
| Text (Specialized) | models.UUIDField() |
Was my blog helpful? Please leave a comment at the bottom. it will be a great help to me!
App promotion
Deku.Deku created the applications with Flutter.If you have interested, please try to download them for free.



