Contents
Blog series
This blog post is a series. You can see the other posts on the link below.
- [MacOS] Flutter installation
- [Flutter] Variable in Dart
- [Flutter] Operator in Dart
- [Flutter] Statement in Dart
- [Flutter] Function in Dart
- [Flutter] Class in Dart
Outline
Flutter is developed using Dart which is developed by Goggle.
- Dart: Official site
In this blog post, I will introduce how to use Dart basically, and how to use Variable in Dart.
You can see the source code, that is introduced on this blog post, on the link below
Development environment
We need to install Flutter to develop the Dart on the local. See the previous blog post to install the Flutter.
This blog post assumes that Flutter has been installed and configured. Let’s create a new folder to use Dart.
mkdir dart
cd dartAnd then, execute the commend below to open VSCode.
code .Hello world
Next, let’s create a Dart file to code with Dart language. click the new file button to create a new file on VSCode.
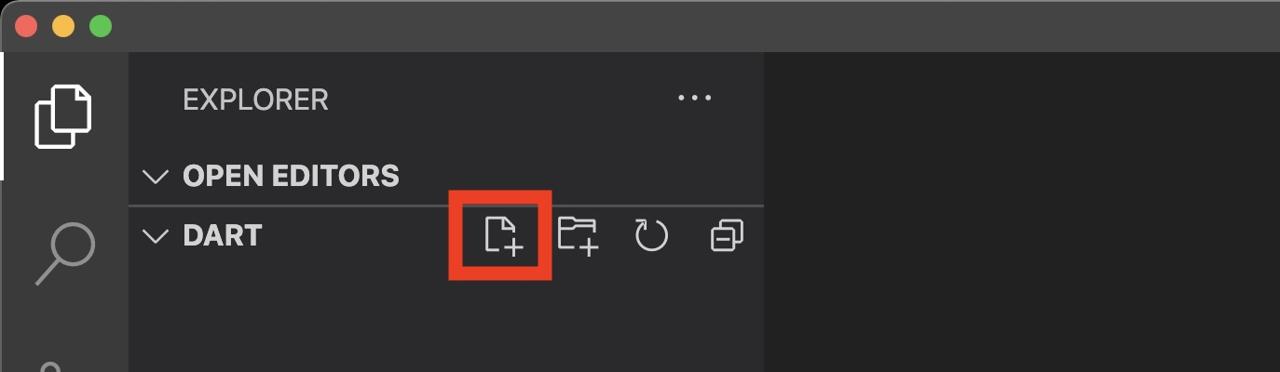
You can use any file name, but I use main.dart here. After creating the new file, open the file and modify it like below.
void main() {
print('Hello world!');
}After modifying all, press cmd + shift + d and search Debug: restart and execute it.
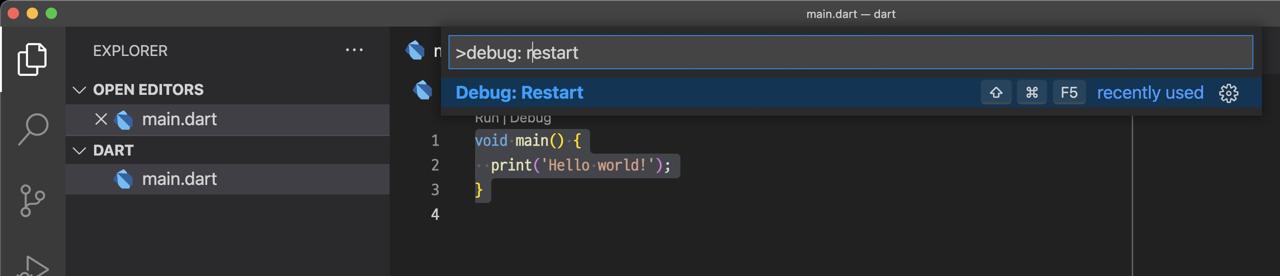
After it, VSCode weill create the .vscode/launch.json file automatically.
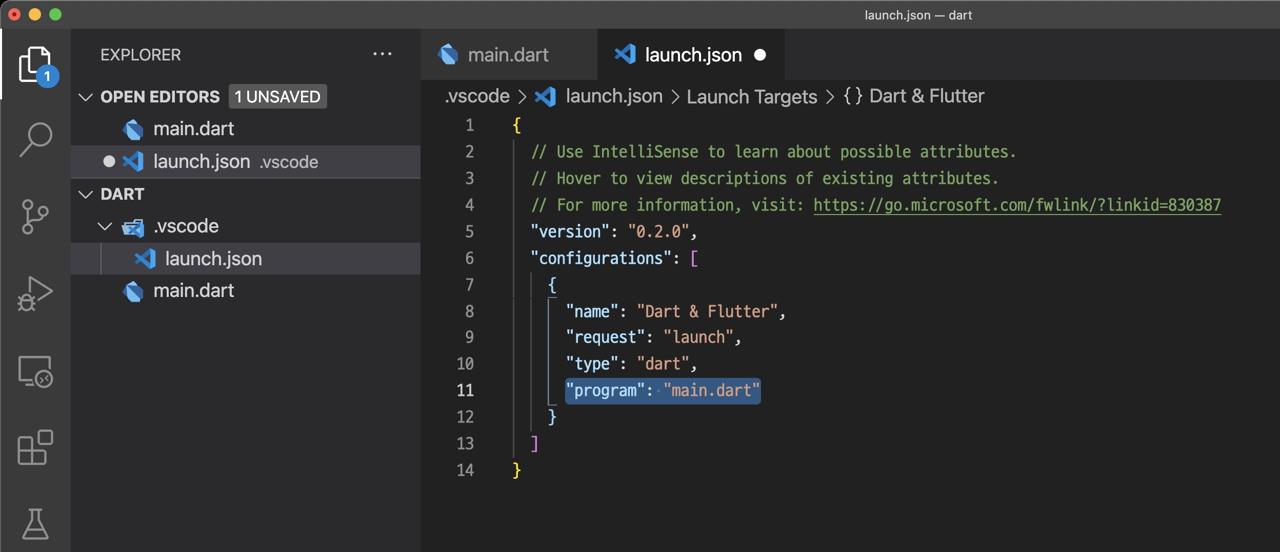
We need to configure the Dart file we’ve created on it. Open the file and modify it like below.
{
...
"configurations": [
{
...,
"program": "main.dart"
}
]
}After modifying, go to main.dart file again, and press cmd + shift + d to execute the debug restart. And then, you can see the Hello world on the DEBUG CONSOLE of VSCode like below.
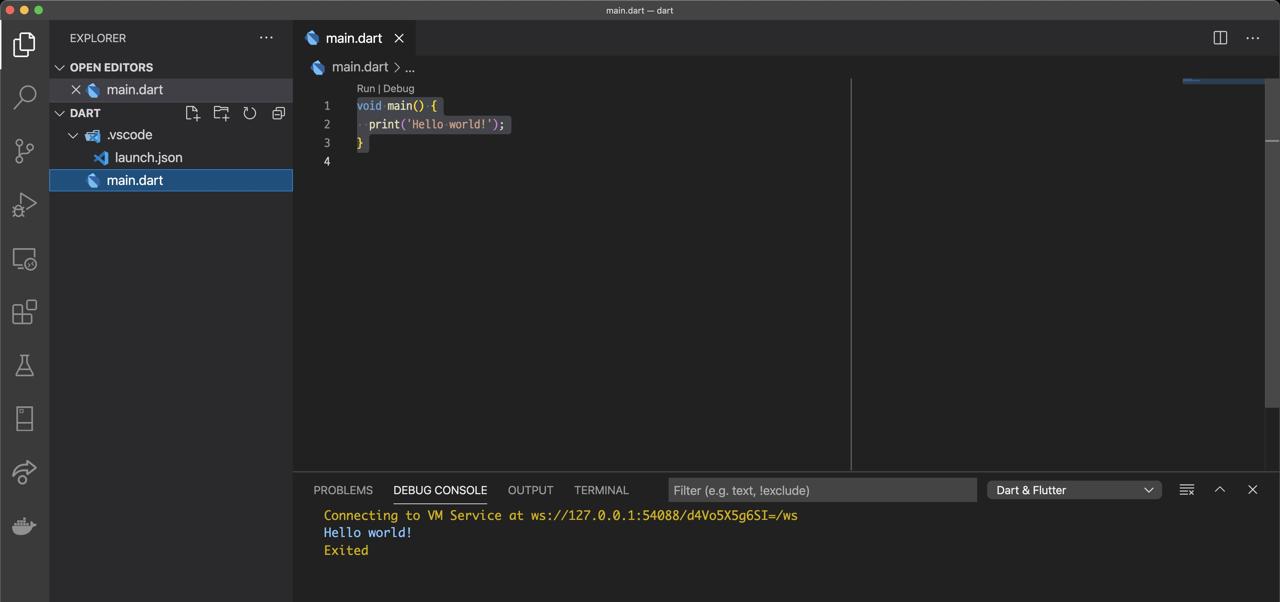
I just skip the explanation of the code.
Variable
Let’s see how to use Variable in Dart.
var
The var type is similar behavior to JavaScript. You can assign any type to this variable.
void main() {
var value1 = 'test';
print(value1);
var value2 = 1;
print(value2);
}If you assign the variable when you define it, Dart fixes the type of the variable. In this case, value will be String type, and value2 will be int type.
After the type is fixed, when you assign other types to it, the error occurs like below.
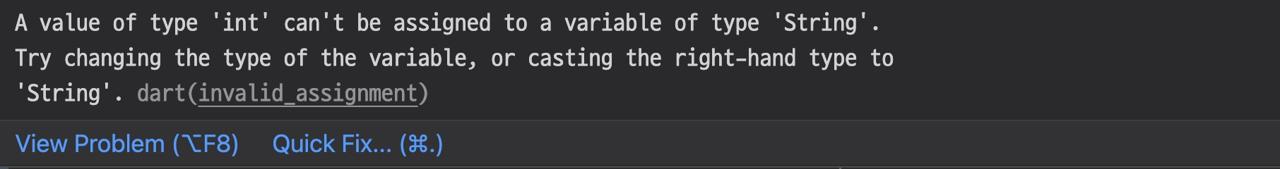
However, if you don’t assign the variable when you define it, the variable will be Dynamic Type and you can set any type to it.
void main() {
var value1;
value1 = 'test';
print(value1);
value1 = 1;
print(value1);
}In this example, we’ve assigned the String type to the variable, and assigned int type to it again. However, the error doesn’t occur unlike before.
int
You can use int type when you use the integer type of the variable.
void main() {
int num1 = 2;
int num2 = 4;
print(num1 + num2);
print(num1 - num2);
print(num1 * num2);
print(num1 / num2);
}You can use basic mathematical operations with int type.
double
You can use double type when you use the real type of the variable.
void main() {
double num1 = 2.2;
double num2 = 4.2;
print(num1 + num2);
print(num1 - num2);
print(num1 * num2);
print(num1 / num2);
}You can use basic mathematical operations with double type.
String
You can use String type in Dart. Note that the String type starts with a capital letter (S) unlike int and double.
void main() {
String name = 'Yakuza';
print(name);
print('Dev ' + name);
print(name.toUpperCase());
print(name.toLowerCase());
}You can use + to combine the strings with String type like other languages, and use various functions.
bool
You can define Boolean variable to store true/false value in Dart.
void main() {
bool wrong = true;
print(wrong);
wrong = false;
print(wrong);
}List
You can define List type data and add the data to it like below.
void main() {
List<String> fruits = [];
fruits.add('Apple');
fruits.add('Banana');
fruits.add('Kiwi');
print(fruits);
fruits.removeAt(1);
print(fruits);
}Also, you can define like below.
void main() {
List<String> fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Kiwi'];
print(fruits);
}Also, you can use it like below.
void main() {
List<String> fruits = List.from(['Apple', 'Banana', 'Kiwi']);
print(fruits);
}You can make a growable list like above, but you can create fixed size list like below.
void main() {
List<String> fruits = List.filled(3, '');
fruits[0] = 'Apple';
fruits[1] = 'Banana';
fruits[2] = 'Kiwi';
print(fruits);
}Note that you can’t use the functions that change the size of List like add and removeAt on the fixed List.
You can create a growable list with List keyword. If you create a list with List keyword like below, you can create the growable list.
void main() {
List<String> fruits = List.empty(growable: true);
fruits.add('Apple');
fruits.add('Banana');
fruits.add('Kiwi');
print(fruits);
}You can use various functions on List.
-
join: join all elements to make one string.
void main() { List<String> fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Kiwi']; print(fruits.join(', ')); } -
indexOf: Search the element and return the index of the element.
void main() { List<String> fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Kiwi']; print(fruits.indexOf('Banana')); } -
where: create a new list with the condition.
void main() { List<String> fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Kiwi']; print(fruits.where((fruit) => fruit.toLowerCase().indexOf('a') >= 0)); } -
forEach: it’s same feature like the for loop.
void main() { List<String> fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Kiwi']; fruits.forEach((fruit) { print('${fruit}!'); }); for (String fruit in fruits) { print('${fruit}!!'); } } -
map: it’s similar with forEach, but the new list is created with the result of the function.
void main() { List<String> fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Kiwi']; Iterable<String> newFruits = fruits.map((e) { return 'My name is ${e}'; }); print(newFruits); print(newFruits.toList()); } -
fold: loop with initial value, and you can use previous value and next value to create a new result.
void main() { List<int> numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; int result = numbers.fold(0, (previousValue, element) { int sum = previousValue + element; return sum * 2; }); print(result); } -
reduce: unlike fold, initial value doesn’t exist, and you should return same type of the element.
void main() { List<int> numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; int total = numbers.reduce((value, element) => value + element); print(total); } -
asMap: change List type to Map type, and the new Map will use the index of the element to the key of the Map. This is normally used when you need to loop the value and you need to use the index of it.
void main() { List<int> numbers = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]; Iterable indexNumbers = numbers.asMap().entries.map((e) { return 'index: ${e.key} / value: ${e.value}'; }); print(indexNumbers); print(indexNumbers.toList()); }
Map
You can store multiple variable to the Map like List, but unlike List, you should store Key Value data on it. The Map uses Key-Value, so the Key should be unique.
void main() {
Map fruitCount = {
'Apple': 3,
'Banana': 4,
'Kiwi': 10,
};
print(fruitCount);
print(fruitCount['Apple']);
}You can define the Map like the List and the, you can add, delete and edit it.
void main() {
Map fruitCount = {};
fruitCount.addAll({
'Apple': 3,
'Banana': 4,
'Kiwi': 10,
});
print(fruitCount);
fruitCount.remove('Apple');
print(fruitCount);
fruitCount['Banana'] = 20;
print(fruitCount);
}Also, You can use the Map like below.
void main() {
Map fruitCount = new Map.from({
'Apple': 3,
'Banana': 4,
'Kiwi': 10,
});
print(fruitCount);
}The Map also provides the various functions. For example, you can collect and print only Key or Value of the Map like below.
void main() {
Map fruitCount = new Map.from({
'Apple': 3,
'Banana': 4,
'Kiwi': 10,
});
print(fruitCount.keys.toList());
print(fruitCount.values.toList());
}You can set the Type to the Map like the List.
void main() {
Map<String, int> fruitCount = {
'Apple': 3,
'Banana': 4,
'Kiwi': 10,
};
print(fruitCount);
}You can loop the Map with entries and make a new List.
void main() {
Map<String, int> fruitCount = {
'Apple': 3,
'Banana': 4,
'Kiwi': 10,
};
Iterable newFruitCount =
fruitCount.entries.map((e) => '${e.key} is ${e.value}!');
print(newFruitCount);
print(newFruitCount.toList());
}enum
You can use enum in Dart like below.
enum Status {
wait,
approved,
reject,
}
void main() {
Status currentStatus = Status.wait;
print(currentStatus == Status.approved);
print(Status.values.toList());
}Constant
Let’s see how to use the constant in Dart.
final and const
You can define the Constant with final and const keyword in Dart.
void main() {
final String firstName = 'Yakuza';
const String lastName = 'Dev';
print(firstName);
print(lastName);
}You can’t modify the variable that is defined the Constant.
void main() {
final String name = 'Yakuza';
name = 'Dev'; << ERROR
print(name);
}The final and const have the difference like below.
- final: the constant is created at runtime.
- const: the constant is created at compile.
void main() {
final DateTime now = DateTime.now();
print(now);
}For example, we can create the constant of the current time with DateTime. However, we can know the current time at runtime, so we can’t use const here.
void main() {
const DateTime now = DateTime.now();
print(now);
}We can know the current time when the program is executed, so we can’t set it at compile.
String Interpolation
You can insert variable to the string in Dart like below.
void main() {
String name = 'Yakuza';
int num = 1;
print('User: (${num}) ${name}');
}If you execute the example, you can see the result like below.
User: (1) YakuzaNullable
All variables were initialized when they were defined. If the variables are not initialized, the error occurs. However, you can define the variable like below without initial value.
void main() {
String? name;
name = 'Yakuza';
print(name);
name = null;
print(name);
}If you use ? to define the variable, you can define the variable without the initial value, and the variable will be set with null. Also, you can assign the null to this variable.
Characteristics of the variable
The variable has the characteristics like below.
-
You can’t define the same name variables.
void main() { String name = 'Yakuza'; String name = 'Dev'; int name = 1; } -
The variable name is started with a lowercase letter and follow Camelcase rule.
-
The variable name can be started with
_, but this variable name is used for the Classprivatevariable name. -
The Class name is started with a uppercase, so if you define the variable name with the uppercase, we can’t recognize the variable and Class with the name.
Completed
We’ve seen how to use the variable of the Dart to develop an app with Dart. Now, you can freely define the variable and constant.
Was my blog helpful? Please leave a comment at the bottom. it will be a great help to me!
App promotion
Deku.Deku created the applications with Flutter.If you have interested, please try to download them for free.



